External Hemorrhoids vs Internal Hemorrhoids – A Complete Guide
Hemorrhoids are a common yet misunderstood medical condition. Millions of people experience them at some point in their lives. However, due to embarrassment or confusion about the symptoms, many suffer in silence without even taking proper treatment.
Hemorrhoids are commonly known as “piles”. They cause swollen veins in the lower rectum and anus. While they are usually not serious, they can cause discomfort. Understanding the difference between external hemorrhoids and internal hemorrhoids can help you identify the symptoms, choose the right treatment, and prevent future occurrences.
In this guide, we’ll break down the two main types of hemorrhoids, their symptoms, causes, and understand how they can be managed and or treated effectively.
What are Hemorrhoids?
Hemorrhoids occur when the blood vessels around the anus or in the rectum become swollen, mostly due to increased pressure. This pressure can come from straining during bowel movements, prolonged sitting, chronic constipation, pregnancy, or heavy lifting.
Hemorrhoids are categorised into two main types based on their locations:
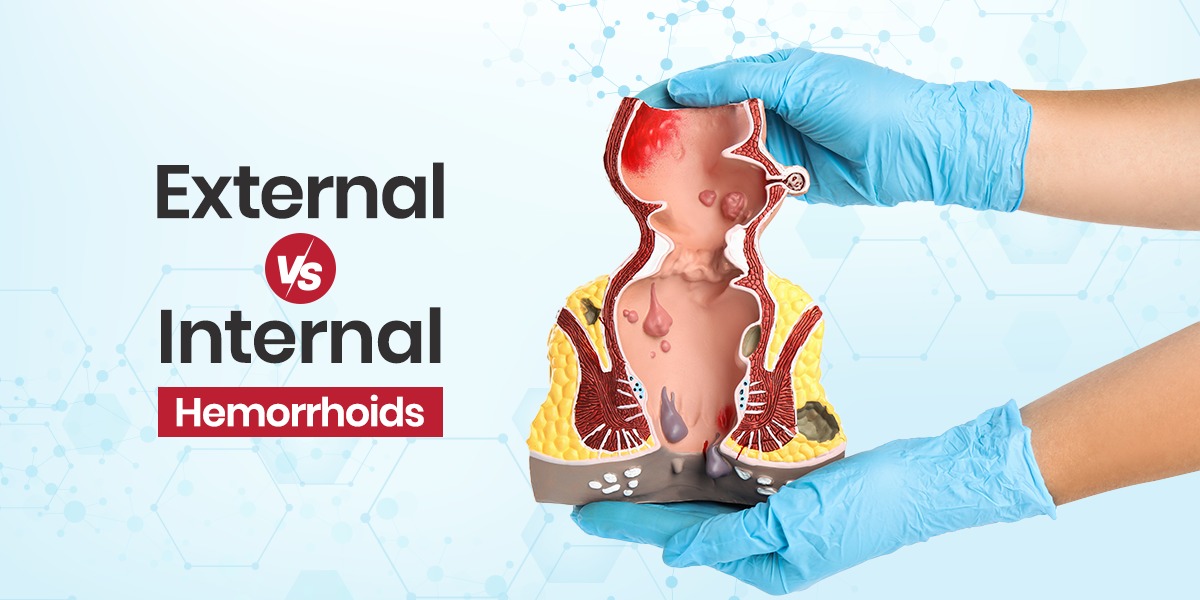
- External hemorrhoids develop under the skin around the anus.
- Internal hemorrhoids develop inside the rectum and are not visible.
Let’s look into them in detail.
External Hemorrhoids
Location
External hemorrhoids form under the skin around the external portion of the anus. Because of this location, they’re easily visible and can often be felt as a lump or swelling near the anal opening.
Symptoms
Let’s now take a look at external hemorrhoid symptoms.
- Itching or irritation in the anal area.
- Pain or burning, especially after or during bowel movements.
- Swelling or hard lumps around the anus.
- Bleeding while passing stools.
- Thrombosed hemorrhoids can cause severe pain and swelling.
Severity
External hemorrhoids can range from mildly irritating to extremely painful. Particularly, thrombosed hemorrhoids can cause intense discomfort and may require minor surgery.
Diagnosis
External hemorrhoids can be diagnosed with a simple physical examination of the anal area.
Internal Hemorrhoids
Location
Internal hemorrhoids develop inside the rectum, above the point where sensory nerves are less active. Due to this, they don’t cause much pain.
Symptoms
Here are some common internal hemorrhoid symptoms:
- Painless rectal bleeding while passing stools.
- Mucus discharge.
- A sensation of incomplete evacuation after bowel movement.
- Hemorrhoids may push through the anus.
Grades of Internal Hemorrhoids
Internal hemorrhoids are classified into four grades depending on how far they have prolapsed:
- Grade I: May experience bleeding without prolapse.
- Grade II: Prolapse during heavy work, but returns by itself.
- Grade III: Prolapse and must be pushed back manually.
- Grade IV: Prolapses permanently and may require surgery.
Diagnosis
A physician may perform a digital rectal exam and use tools like an anoscope or proctoscope to view the inside of the rectum.
Causes
Both external and internal hemorrhoids are usually caused by increased pressure in the lower rectum. Here are some causes of hemorrhoids:
- Straining bowel movements.
- Sitting for long periods, especially on a toilet seat.
- Chronic constipation or diarrhea.
- Heavy lifting.
- Pregnancy and childbirth.
- Low fibre diet.
- Obesity.
- Aging can make the tissue supporting the veins in your rectum and anus weak.
- Genetic factors also play a role.
Treatment Options for Hemorrhoids
Both external and internal hemorrhoids often respond well to home remedies, especially in the early stages. Here are some commonly recommended treatments.
Home Remedies
- Sitz baths (warm water bath for 10-15 minutes, many times a day).
- Cold compress to reduce swelling.
- Creams or ointments.
- Wipes with soothing ingredients like aloe vera.
- Including high-fibre diets like fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains.
- Stay hydrated to soften the stool.
- Avoid sitting for too long.
Medical Treatments
- Rubber Band Ligation: This method cuts off the blood supply to the hemorrhoid, causing it to shrink.
- Scelerotherapy: This is an injection that shrinks the hemorrhoids.
- Infrared Coagulation (IRC): This method uses heat to shrink the blood vessels.
- Laser Therapy: This is a minimally invasive and effective treatment.
Surgical Treatments
- Surgery may be necessary for large, persistent, or severely prolapsed hemorrhoids, especially in Grade III or IV.
- Hemorrhoidectomy: Surgical removal of the hemorrhoids. This is very effective but may require recovery time.
- Stapled Hemorrhoidopexy: Repositions internal hemorrhoids and cuts off the blood supply. This is less painful than traditional surgery.
Conclusion
Hemorrhoids are a common and uncomfortable problem. However, they’re highly treatable and preventable. Whether you’re dealing with the pain of external hemorrhoids or the bleeding from internal ones, understanding the differences will help you treat them properly. With the right combination of self-care, lifestyle changes, and medical intervention, most people can manage their symptoms and prevent future breakouts.
Hemorrhoids can be managed with the right support. Book a consultation with the best gastroenterologist in Lucknow at Regency Healthcare and take the first step towards relief.
Also Read: How to Beat Irritable Bowel Syndrome: Expert Tips You Need to Know

 Call-an-Ambulance
Call-an-Ambulance



