Know all about lymphoma – Types, Symptoms, Treatment

What is lymphoma
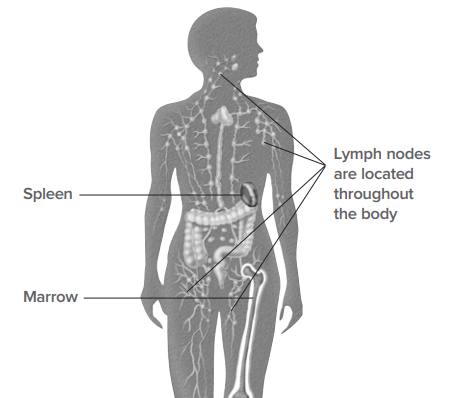
Lymphoma is a cancer of lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell. Lymphocytes are part of body’s immune system and are found in the blood stream, lymphatic system, spleen, lymphnodes and bone marrow. When lymhocytes become malignant, they multiply and form tumorous growth also known as lymphoma.
Overview of structural distribution of normal Immune system.
What are the types of lymphoma
Lymphomas encompass two types of neoplasms
- Hodgkin lymphoma
- Non Hodgkin lymphoma
Hodgkin lymphma: These type of lymphomas are characterised by slow frowth and contigous lymph node involvement
Non Hodgkin Lymphoma
There are more than 30 different types of NHL’S which can be broadly classified into 3 types
- Low grade or indolent lymphoma: These are characterised by painless swelling of lymphnodes usually in neck in an otherwise healthy individual
- Aggressive NHL: These types of lymphoma grow more rapidly than low grade lymphoma. Apart fro pain and swelling in neck, axilla, groin or abdomen these patients may also have fever or weight loss
- High garde NHL: These lymhomas grow very rapidly and thus have aggressive symptoma depending upon the organ of involvement.
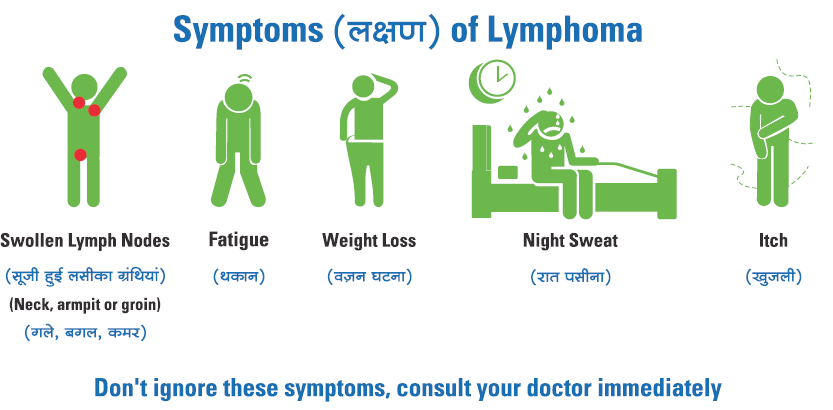
Symptoms of lymphoma
What are the common tests used for diagnosis and staging of lymphoma
- Lymph node biopsy: It is the most important diagnostic test which tells about the type of lymphoma
- Computerised axial tomography (CT scan): CT scan of chest and abdomen can be used for staging of disease
- Positron Emission Tomography (PET scan): PET scan is the preferred imaging modality for inital staging as well as response to therapy
- Bone marrow biopsy: A thin needle is inserted into hip bone and small sample of blood and tissue is collected to confirm involvement of bone marrow by lymphoma
- Blood tests: Blood tests are performed to determine if various blood cells and biochemistries are within normal limits
Treatment Of Lymphoma:
CHEMOTHERAPY: Chemotherapy is the main modality of treatment of lymphoma. Chemotherapy means treatment of cancers with drugs that kill cancer cells. Chemotherapy drugs work by stopping division of cancer cells or by triggering death of cancer cells. Many different combinations of cytotoxic drugs are given in form of cycles for treatment of lymphomas. Most chemotherapy treatments are given on outpatient basis but some protocols may require hospital stay.
BIOLOGICAL THERAPIES: Biological therapies are treatments which act on cell processes and stop cells from growing and dividing. These are useful to treat lymphomas. Monoclonal antibodies are the most common biological therapies used in lymphoma treatment. These are proteins made from single copy of humanised antibody that target particular protein found on cancer cell surface.
RADIOTHERAPY: Depending on which type and stage of lymphoma you have, your treatment might involve radiotherapy alone, or in combination of chemotherapy.
Some types of lymphoma that are low grade or ‘indolent’ (slow-growing) can be cured with radiotherapy alone if they are at an early stage.
High-grade lymphomas that are early stage are often treated with chemotherapy followed by radiotherapy.
STEM CELL TRANSPLANT: Some people need high doses of chemotherapy to treat their lymphoma. High doses of chemotherapy can be very effective at killing lymphoma cells but they can cause permanent damage to your bone marrow. Patients can be given healthy blood stem cells after high-dose chemotherapy to avoid the harmful effects of high dose chemotherapy, this is called a stem cell transplant.
Stem cell transplants are used in lymphoma treatment in different situations but mainly when:
- Lymphoma has relapsed(come back) after treatment
- Lymphoma is refractory (doesn’t respond) to treatment
- As part of first treatment if lymphoma is likely to relapse (high risk).
Nutrition in lymphoma in cancer patients:
Good nutrition is especially important for people with cancer. Eating a variety of foods and well-balanced meals can help you feel better and stay stronger. Eating well during treatment helps to maintain your body weight, improve your strength and energy, decrease the risk of infection and assist your body in healing and recovery from cancer treatments. Some cancer treatments work better when you are well nourished. People with cancer who are well nourished and able to maintain a healthy body weight often have a better prognosis. A healthy diet includes eating and drinking foods and liquids with nutrients that your body needs – proteins, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins, minerals and water
Some Key Do’s And Dont’s For Patient Of Lymphoma On Treatment
DO’S
- Make sure you tell your doctor about any other medications that you are taking.
- Inform your doctor that you are pregnant or may be pregnant befor starting treatment
- Maintain good nutrition
- Contact your doctor immediately in case of fever >100°f
- Avoid crowded places and people with active infections (cold, flu, diarrhea, vomiting, chickenpox etc)
- Ensure proper hygeine, wash your hands regularly before every meals and after using toilets.
- Food hygeine is important. Consume only well cooked and fresh food.
DONT’S
- Do not receive any kind of vaccination or immunisation without your doctor’s approval
- Do not undergo invasive procedures like tooth extraction or other procedures without your doctor’s approval
- Do not breastfeed while taking chemotherapy
- Do not eat stored food, do not reheat food
–By Dr. Priyanka Verma, Consultant Hemato Oncology
Regency Hospital Tower -2
Reception no: 0512 – 3362525

 Call-an-Ambulance
Call-an-Ambulance



