What is Angioplasty? Procedure, Stent, and Recovery Explained
Introduction
Angioplasty is a minimally invasive procedure used to open narrowed or blocked blood vessels. The term “angio” means blood vessels, and “plasty” means to form. Angioplasty aims to restore normal blood flow to reduce the risk of a heart attack. It has become one of the most common and effective treatments for coronary artery disease (CAD). Let’s understand more in detail.
What is Angioplasty?
Our heart requires a constant supply of blood rich in oxygen to function properly. When plaque, made of fat, cholesterol, and other substances, accumulates in the arteries, it reduces blood flow to the heart. If a plaque ruptures and forms a blood clot, it can suddenly stop blood flow, resulting in a heart attack.
Angioplasty helps reopen these narrowed arteries, improving circulation and reducing the risk of future cardiac problems.
Angioplasty Procedure
Here’s the step-by-step overview of the angioplasty procedure.
- Preparation: The patient is given a mild sedative to help them relax, but usually remains awake.
- Catheter Insertion: A thin, flexible tube called a catheter is inserted into the artery and guided towards the heart using X-ray imaging.
- Dye Injection: A special dye is injected through the catheter to make the blood vessels visible on the X-ray. This helps to locate the exact site of the blockage.
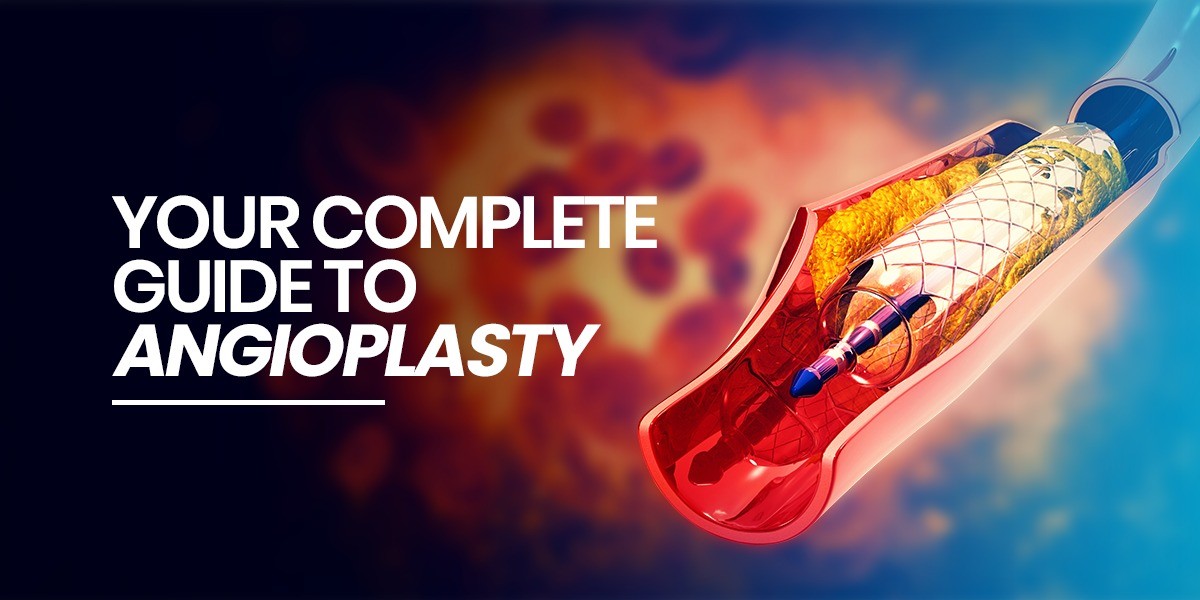
- Balloon Inflation: Once the catheter reaches the blocked area, the doctor threads a thin tube with a tiny balloon at its tip through it. The doctor then gently inflates the balloon for a few seconds to press the plaque against the artery walls.
- Stent Placement: In most cases, an angioplasty stent (a small mesh tube) is placed at the site of the blockage to keep the artery open after the balloon is removed.
- Completion: After ensuring good blood flow through imaging, the catheter is removed.
What is a Stent and Why is It Used?
A stent is a small, expandable metal or polymer mesh tube that supports the artery walls and prevents them from narrowing again after angioplasty. It is used to lower the chances of the artery closing again.
Recovery After Angioplasty
Recovery after angioplasty is typically faster than from open-heart surgery, but proper care is essential.
- After angioplasty, doctors monitor their heart rhythm and blood pressure.
- To prevent bleeding, they are advised to lie flat for some hours.
- Most patients can eat and drink a few hours after the procedure.
- Many patients get discharged within 24-48 hours, depending on their condition.
- After coming home, patients must avoid strenuous activities for several days.
- The insertion site must be kept clean and watched for signs of infection.
- Take medications regularly and follow a heart-healthy diet.
- For long-term benefits, quit smoking and alcohol consumption.
- Do light exercise prescribed by your doctor.
Conclusion
Angioplasty is a life-saving procedure that has transformed the way doctors treat heart blockages. By using a minimally invasive method, it quickly restores blood flow, relieves chest pain, and reduces the risk of a heart attack. Early recognition of heart symptoms, timely medical attention, and proper health management will help keep your heart strong and arteries clear.
Looking for the best cardiologist in Gorakhpur? Visit Regency Hospitals, a multispeciality hospital with experienced doctors, high-end healthcare technology, and all under one roof.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is angioplasty a serious surgery?
Though angioplasty is not considered a major surgery, it is a serious medical procedure. It is a minimally invasive procedure that involves inserting a thin tube through an artery in the wrist or groin. It does not require making large incisions in the chest.
How long will angioplasty last?
Angioplasty can last for many years. However, the exact duration depends on the patient’s overall health and lifestyle habits. For a long-lasting result, the patient must take prescribed medications regularly, follow a healthy diet, quit smoking, limit alcohol, exercise regularly, and manage conditions like diabetes, high cholesterol, and high blood pressure.
What is the risk age for angioplasty?
There is no specific age risk for angioplasty. It is usually considered a safe procedure if done by an expert. But some studies show that patients over 65 years are at a higher risk of developing complications.
How painful is angioplasty?
Generally, angioplasty is not very painful. Since it is done under local anesthesia, patients do not feel the pain. But some people may feel pressure or a pushing sensation when the balloon is inflated to open the blockage. After the procedure, one might feel tenderness or bruising at the catheter insertion site.
How much does angioplasty cost?
The cost of angioplasty varies depending upon the hospital, the type, and the number of stents used. In most Indian hospitals, the cost of angioplasty ranges from 1.5 lakh to 4.5 lakh.
Read More: How to Prevent Heart Disease: Causes, Symptoms & Treatments

 Call-an-Ambulance
Call-an-Ambulance



