Heart Stent Operation: Step-by-Step Procedure and Recovery Guide
Heart-related problems have become increasingly common due to lifestyle changes, stress, and underlying medical conditions such as diabetes and high blood pressure. One of the most effective and widely performed treatments for blocked heart arteries is the Heart Stent procedure. It helps restore proper blood flow to the heart, reducing the risk of heart attacks and improving quality of life.
What Is a Heart Stent?
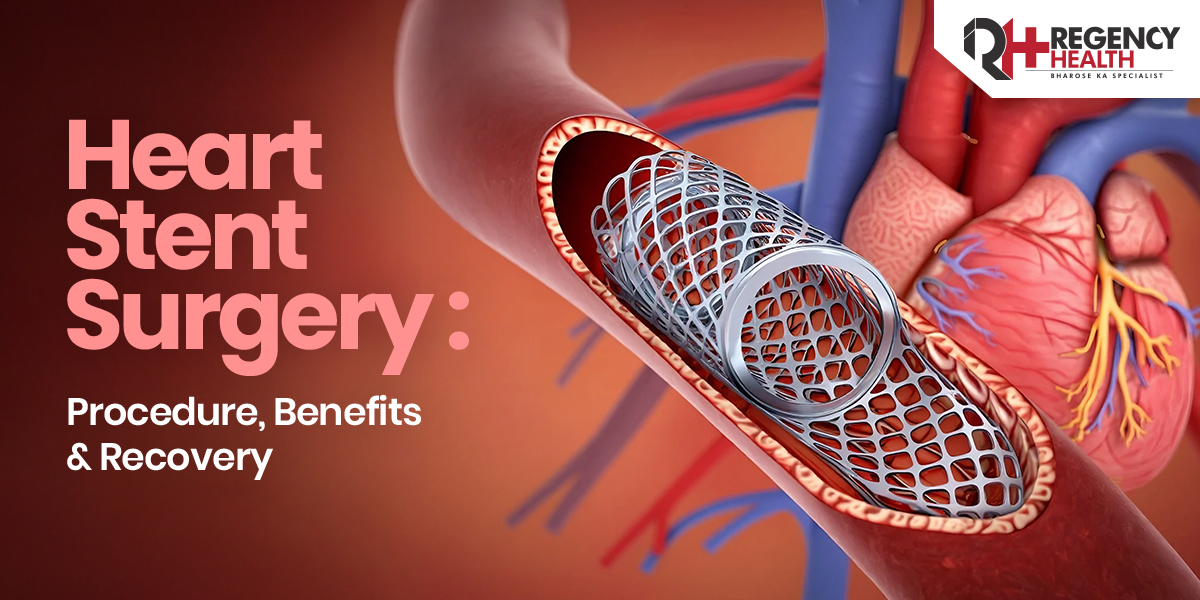
If you are wondering what is a heart stent, it is a small, expandable metal mesh tube placed inside a narrowed or blocked coronary artery. Its purpose is to keep the artery open so that oxygen-rich blood can flow freely to the heart muscle.
A Heart Stent is usually placed during a minimally invasive procedure called angioplasty. Most modern stents are drug-eluting, meaning they slowly release medication to prevent the artery from narrowing again.
Why Is a Heart Stent Needed?
Heart arteries can become blocked due to the buildup of fatty deposits known as plaque. This condition is called coronary artery disease (CAD). When blood flow is restricted, it can cause chest pain (angina), shortness of breath, or even a heart attack.
Doctors may recommend a Heart Stent if:
- One or more coronary arteries are significantly narrowed
- Symptoms persist despite medications
- There is a risk of heart attack
- Emergency treatment is needed during a heart attack
In some cases, patients may require 3 stents in heart if multiple arteries are blocked.
Symptoms Indicating the Need for a Heart Stent
Common warning signs include:
- Chest pain or tightness
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue during mild activity
- Pain radiating to the arm, jaw, or back
- Dizziness or sweating
Early diagnosis and timely intervention can be lifesaving.
Heart Stent Operation: Step-by-Step Procedure
The heart stent operation is performed by an interventional cardiologist in a cardiac catheterization lab. It usually takes 30 minutes to 2 hours.
Step-by-Step Heart Stent Operation Explained
The heart stent operation is a minimally invasive procedure that restores blood flow to the heart. It is usually performed in a specialized cardiac catheterization laboratory and does not require open-heart surgery. Below is a detailed explanation of each step to help patients understand what to expect.
Step 1: Local Anesthesia
The procedure begins with the administration of local anesthesia, usually at the wrist (radial artery) or groin (femoral artery). This numbs the area so the patient does not feel pain during catheter insertion. The patient remains awake and comfortable throughout the procedure.
Step 2: Catheter Insertion
A thin, flexible tube called a catheter is gently inserted into the blood vessel through the numbed area. Using advanced imaging guidance, the cardiologist carefully navigates the catheter through the blood vessels until it reaches the heart’s coronary arteries.
Step 3: Contrast Dye Injection
Once the catheter is in place, a contrast dye is injected through it. This dye makes the coronary arteries visible on X-ray images, allowing the doctor to clearly identify the location, severity, and number of blockages that are restricting blood flow.
Step 4: Balloon Angioplasty
After identifying the blockage, a small balloon attached to the catheter is positioned at the narrowed section of the artery. The balloon is then gently inflated, compressing the plaque against the artery walls and widening the passage to improve blood flow to the heart muscle.
Step 5: Stent Placement
A stent mounted on the balloon is expanded along with the balloon. Once the artery is opened, the stent locks into place and acts as a supportive scaffold to keep the artery open. The balloon is then deflated and removed, leaving the stent permanently in position.
Step 6: Restoration of Blood Flow
With the stent securely placed, blood flow through the artery is restored. The cardiologist checks the artery to ensure proper circulation and then carefully removes the catheter. A small bandage is applied to the insertion site.
Most patients remain awake during the heart stent operation and experience only mild pressure or discomfort. The procedure is generally safe, quick, and highly effective in relieving symptoms such as chest pain and breathlessness.
How Many Stents Can Be Placed?
Depending on the severity of blockages, more than one stent may be required. Placing 3 stents in heart is not uncommon and can be done safely in a single or multiple procedures.
The number of stents depends on:
- Number of blocked arteries
- Location of blockages
- Patient’s overall heart health
Recovery After Heart Stent Operation
Recovery after a Heart Stent procedure is generally quick, but proper care is essential.
Immediate Recovery
- Hospital stay of 1–2 days
- Monitoring of heart rhythm and blood pressure
- Mild soreness at catheter insertion site
At-Home Recovery
- Resume light activities within a few days
- Avoid heavy lifting for at least a week
- Take prescribed medications regularly
- Follow heart-healthy lifestyle changes
Most people return to normal activities within 1–2 weeks.
Lifestyle Changes After Heart Stent Placement
A stent treats the blockage, but lifestyle changes prevent future problems.
Key recommendations include:
- Quit smoking
- Eat a heart-healthy diet
- Exercise regularly as advised
- Control blood pressure and diabetes
- Manage stress
These steps help extend the life of the Heart Stent and improve long-term outcomes.
Risks and Complications of Heart Stent
Although generally safe, the heart stent operation may carry some risks, including:
- Bleeding at insertion site
- Blood clots inside the stent
- Infection (rare)
- Restenosis (re-narrowing of artery)
Strict adherence to medications, especially blood thinners, significantly reduces these risks.
Importance of Expert Cardiac Care
Heart conditions need timely diagnosis and precise medical attention to prevent complications. Expert cardiac care helps in accurately identifying the severity of heart disease and selecting the most appropriate treatment based on an individual’s condition. Proper monitoring during and after procedures such as stent placement also plays a key role in ensuring safe recovery and long-term heart health.
An experienced cardiology team brings together clinical expertise and advanced diagnostic tools to deliver personalized care. Consulting the best cardiologist in Lucknow at Regency Hospitals enables patients to receive well-planned treatment, close follow-up, and guidance focused on improving overall heart function and maintaining a healthy, active life.
Conclusion
A Heart Stent procedure has revolutionized the treatment of coronary artery disease by offering a safe, effective, and minimally invasive solution. Understanding what a heart stent is, how the procedure works, recovery expectations, and cost considerations empowers patients to make informed decisions. With timely treatment, expert care, and healthy lifestyle choices, patients can enjoy improved heart health and a better quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is a heart stent used for?
A heart stent is used to open blocked coronary arteries and restore blood flow to the heart.
Is heart stent operation painful?
The procedure is minimally invasive and usually causes little to no pain.
Can a person live normally after a heart stent?
Yes, with medications and lifestyle changes, most people live normal, active lives.
How long does a heart stent last?
Modern stents are designed to last a lifetime, provided proper care is taken.
What is the average heart stent cost in India?
The heart stent cost in India typically ranges from ₹1.5 to ₹3.5 lakhs, depending on several factors.
Read More:
- 4 Simple Ways to Keep Your Heart Healthy
- 10 Ways to Improve Your Heart Health
- How to Prevent Heart Disease: Causes, Symptoms & Treatments
- Heart Failure: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments

 Call-an-Ambulance
Call-an-Ambulance



